To help blog posts and pages gain search visibility, you need to use on-page SEO to attract search engines and help them understand, recognize, and rank your content. To help you through that process, we created an on-page SEO checklist. That way you never miss an opportunity to optimize your webpages or blog posts.
Download our free on-page SEO checklist (which also includes steps for optimizing off-page and technical SEO) now. Then use the rest of this post to learn how to execute on-page SEO effectively.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing individual pages of content to earn better ranks in search and drive relevant traffic. It includes tactics that help a single page rank for a primary target keyword.
While on-page SEO relates to optimizing a single page of content, it is also supported by other types of SEO. On-page SEO alone may not be enough to get a page to rank. You also need an off-page and technical SEO strategy to help your overall site look more attractive to search engines if you want to get a page of content to rank.
The rest of this post includes a 33-point on-page SEO checklist, plus important off-page and technical SEO tactics you need to support your on-page efforts.
33-Point On-Page SEO Checklist
Use this SEO task list before you publish any new posts or pages on your site. You can also use the on-page SEO checklist to go back and check your work on any previously published content.
Use this on-page SEO task list before you publish any new posts or pages on your site.
1. Perform keyword research to find the top keywords.
On-page SEO starts with finding the best keyword for a particular page of content. The best keyword is the phrase or term that:
- Is relevant to the main topic or theme of the content. The keyword should be an accurate description of your content.
- Is regularly searched for by your target audience. The search volume for the keyword is large enough to drive traffic to your site from your ideal target market.
- Is within your site’s competitive power. Your site has enough authority to rank above other sites already ranking for that keyword.
2. Choose one primary keyword for your content.
Once you choose your keyword, assign it to one page of content on your site. Create an editorial calendar for new content and assign a target keyword to each page.
3. Make sure the primary keyword isn’t assigned to another piece of content.
A primary keyword should never be assigned to more than one page of content on your site. If you assign the same keyword to more than one page, it can cause keyword cannibalization issues, wherein search engines don’t know which page is more important and, therefore, rank neither page. You can use a duplicate content checker to find issues like this on your site.
4. Choose three to five related keywords for your content.
Related keywords are terms and phrases that are synonyms or semantically related to your primary keyword. They are sometimes referred to LSI keywords or latent semantic indexing keywords. Perform keyword research to find three to five keywords that are related to your primary keyword.
5. Create a content plan for your keyword.
Once you have your primary keyword, develop a content plan for how you’ll use it. Decide if the keyword should be a timely blog post, evergreen content, or a landing page. Decide how long the content should be and how you want the content to support your marketing funnel.
- Match the content to the keyword search intent. Create content that provides what the user would be looking for when they perform the search.
- Decide where the content fits in your sales funnel. Use a customer journey mapping template and create content that fits into a specific purchase funnel level.
- Create content that is better than currently ranking content. Review content that currently ranks for your keyword. Try to create a page that is more valuable, better organized, contains original data, etc..
6. Write a title that includes the primary keyword.
Write a title that is appealing to both search engines and audiences. Serve search engines by including the primary keyword near the beginning of the headline, and serve audiences by writing a descriptive yet concise title that tells readers why the content is valuable.
Read more: 12 Tips for Writing Headlines Readers (and Search Engines) Can’t Resist
7. Wrap the title in an H1 tag.
Add the title to your page, and wrap it in an H1 title tag. An H1 title tag is a piece of HTML code that tells search engines that the copy is the title of the page and an important description of the content.
8. Write more than 300 words of body content.
The number of words for your content will vary depending on the page’s purpose and the depth of the topic. But as a best practice, publish pages that have more than 300 words of body copy. Aim for at least 800 words when possible, as more detailed posts will have a stronger probability of ranking.
9. Write original content.
Craft copy that is original and not copied from other sources. Do not copy content that is already published on your site or published on any other sites. Search engines may penalize your site or not rank your page if it has content that is copied or duplicated from other sites.
10. Write high-quality content.
Even when you create SEO content for the purpose of ranking, always remember that your number one focus should be your readers. Create high-quality content that is valuable, useful, and well-written.
Read more: The Complete Guide on How to Write Content for a Landing Page
11. Write for an eighth-grade reading level.
Writing high-quality content doesn’t mean writing like it’s a college-level research paper. In fact, it means the opposite. Write your content for an eighth-grade reading level on the Flesch Reading Scale. That means using common terminology (not complex industry jargon) and writing short sentences and paragraphs.
Writing high-quality content doesn’t mean writing like it’s a college-level research paper. In fact, it means the opposite.
12. Add the primary keyword to create a 2-3% keyword density.
Help search engines recognize the main theme of your content by using the primary keyword throughout the copy. As a best practice, use the term two to three times per 100 words to create a 2-3% keyword density. Try to avoid going over this limit to avoid keyword stuffing issues.
13. Use each related keyword at least once in the body copy.
Refer back to your related keyword list and include each keyword at least once in your copy. Naturally incorporate them into your content; don’t force it.
Here are some general guidelines from Orbit Media for incorporating your target keyword into your post:
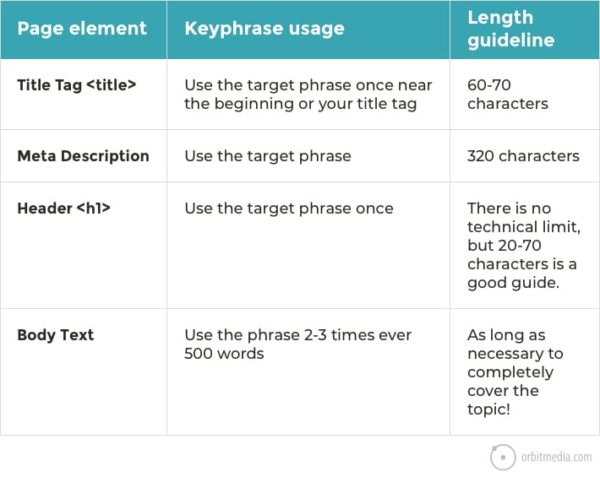
14. Make your content scannable.
Both readers and search engines like content that is easy to scan and understand. Go through your content and use formatting that makes it easy to quickly scan and review.
Break content into sections with descriptive subheadings.
Use bullet points for lists of information.
Use bold formatting or callouts to highlight important points.
Both readers and search engines like content that is easy to scan and understand.
15. Wrap subheadings in an H2 tag.
Help search engines identify the subheadings in your content (and the main points of your copy) by wrapping the phrases in an H2 tag. Like the H1 tag used on your headline, this HTML code tells search engines that the copy is important and related to the primary page topic.
16. Use the primary keyword in at least one subheading.
Tie your content back to the main keyword by using the primary keyword in at least one of your subheadings. Use it in more than one subheading if it is natural and makes sense.
17. Use the primary keyword in the first and last paragraph of the content.
Show search engines that the page is closely related to the topic by bookending your copy with a mention of the primary keyword. Try to use the target keyword near the beginning of your first paragraph and within your final paragraph to reinforce what your content is about. This will help make it clear to search engines why your content is relevant
18. Add relevant internal links using targeted anchor text.
Links help search engines connect and understand online content. Add relevant internal links to other pages on your site, and when possible, use the linked page’s target keyword as the anchor text for the link.
19. Add relevant links to high-quality sites.
Links leading to other sites also add context that helps search crawlers understand your content. So also include relevant, valuable, and high-quality outbound links that lead to other pages when you mention a resource or cite a source within your content
20. Set outbound links to open a new page.
When a user clicks a link on your page, you don’t want them to leave your site completely. Set each outbound link to open in a new window so that your website remains open even if the user temporarily visits another site.
21. Add at least one image.
Make the content more interesting to readers and show search engines that the content is valuable by adding at least one image to the page.
22. Add the primary keyword to the image file name.
Before you upload the image to your website, name the file with a phrase that includes the primary keyword for the page.
23. Add the primary keyword to the image title.
When you upload the image, also add the primary keyword to the image title assigned to the graphic.
24. Add the primary keyword to the image alt tag.
In one final place, add the primary keyword to the image alt tag for the graphic.
25. Size the image properly.
Check the size of your image and make sure it’s not so large that it will slow down site loading times. Compress large files before you upload them to your site, and resize images to the intended display size.
Read more: Image SEO: How to Expertly Optimize Website Images for SEO
26. Write an SEO-friendly URL that includes the primary keyword.
Create a URL for the page that includes the primary keyword. Avoid adding any stop words, special characters, or unnecessary words in the permalink.
Read more: How to Write an SEO-Friendly URL Using the Best Keywords
27. Assign relevant tags and categories (if it’s a blog post).
Blog post tags and categories organize on-site content and help search engines understand topics. If you publish a blog post, add categories and tags that are relevant to the theme of the content.
28. Add an optimized meta title.
A meta title is a line of code that tells search engines the title of a page. It is also the title that appears on search engine results pages (SERPs). Add a meta title for your page that has fewer than 60 characters, includes the primary keyword near the front of the title, and entices the user to click.
29. Add an optimized meta description.
A meta description is a blurb of information that supports the meta title. It also helps search engines understand the content and is displayed on SERPs. Add an optimized meta description that has fewer than 320 characters, includes the primary keyword near the front of the description, and includes a soft call to action encouraging readers to click.
30. Add structured data markup.
To make the page’s SERP results look even more enticing, add structured data markup or schema to your page. Structured data are extra code that helps search engines recognize specific categories of copy within your content. This extra code can lead to a boost in SEO visibility as well as rich search results.
31. Add social sharing links.
Content is more likely to be found when it is optimized for both search and social. Include sharing buttons, and add click-to-tweet and other social sharing call to actions on the page.
32. Proofread your content.
Before you publish a post or page, always proofread the content for spelling and grammatical errors.. This is an essential part of writing, as it makes sure your content is high-quality, authoritative, and worthy of being a top search result.
33. Check your work.
Check on-page SEO one more time before you finish your work. Use a tool like Alexa’s On-Page SEO Checker to scan your content and ensure that you hit every action item on your on-page SEO checklist.
On-Page SEO Tools
Going through this on-page SEO checklist is much easier when you have the following on-page SEO tools to help with research, writing, and optimization.
This 33-step on-page SEO checklist will help you optimize your content so it sends clear signals to search engines and improves your visibility on SERPs.
You need a complete SEO checklist that hits all of the best practices for SEO if you want to boost your site’s overall ability to rank in search. That means adding a technical and off-page SEO checklist to your plans.
To get a full SEO task list of everything you need to optimize your website, download our complete SEO checklist. It includes 50+ action items related to on-page, off-page, and technical SEO.
Download Your Complete SEO Checklist
Basic SEO for websites should include every task on this on-page SEO checklist, as well as the best practices mentioned for off-page and technical SEO. Hit all of these important marks in your SEO strategy by downloading our free SEO checklist PDF. Then, sign up for a free trial of Alexa’s Advanced Plan to access keyword research tools and in-depth SEO reports that help you build and improve your SEO strategy.




